Crustaceans as live food in the aquarium for fish and co
Crustaceans are a real superfood for small and also large fish, and aquarium invertebrates such as shrimps, crabs and prawns can also benefit from them. Their composition of nutrients and fiber is almost perfect. It is optimal to feed crustaceans from saltwater - this way freshwater animals cannot pick up parasites, and many pathogens also do not make the jump from salty to sweet.
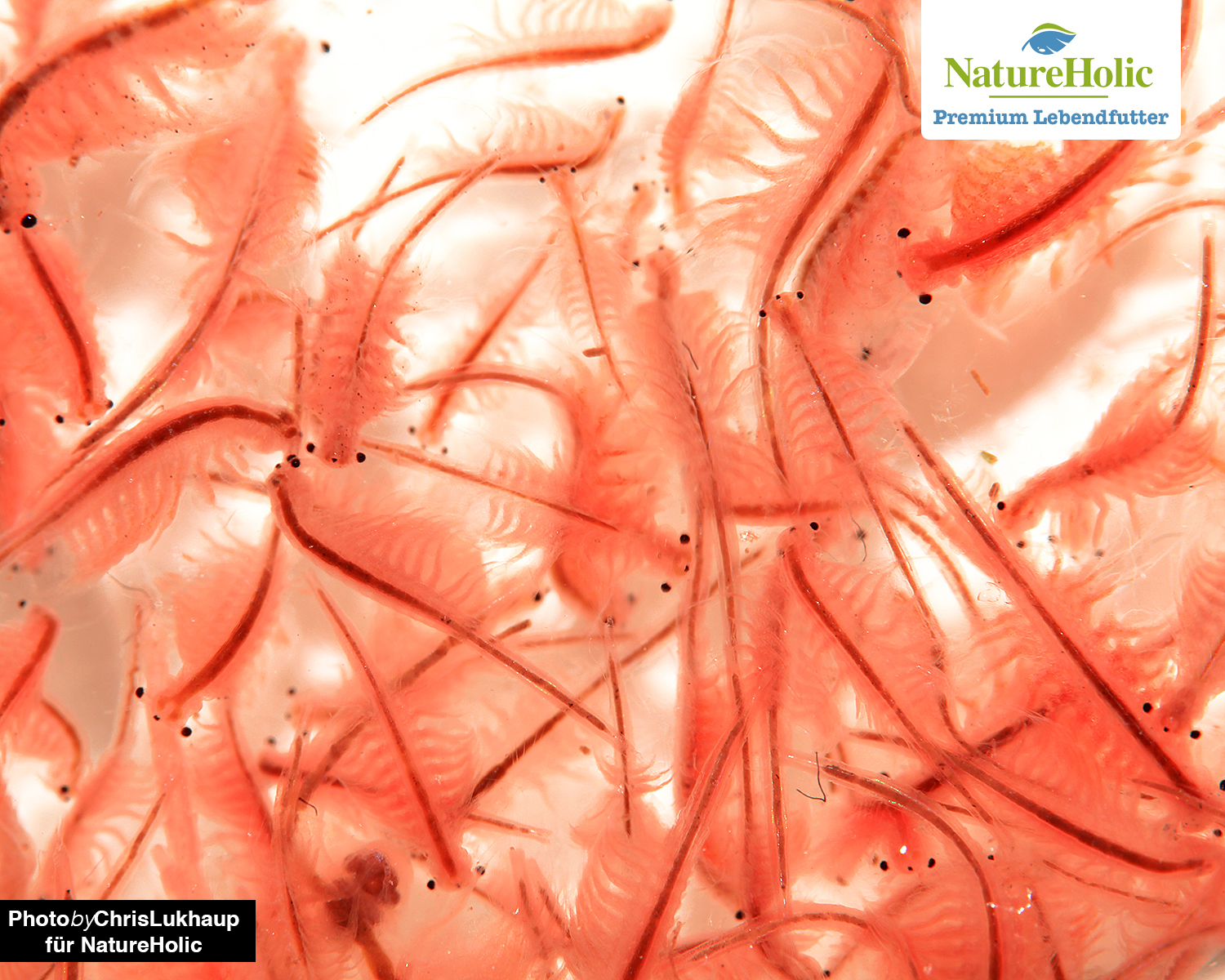
Adult Artemia(buy) and Artemia nauplii(buy)
Artemia are brine shrimp found in inland waters that have very high salinity and highly alkaline water - with salinity well above that of seawater, up to 70 g/l. Here the crayfish have had little competition for millions of years, because practically no other living creatures can exist in this hostile environment. This is one of the reasons why they are so popular in aquaristics, because you cannot catch parasites with Artemia.
Different species
There are different species in the genus Artemia. For example, Artemia salina comes from the Mediterranean region, to whose high content of astaxanthin the flamingos there owe their red color. And we all know Artemia nyos or Sea Monkeys - as a gimmick in the Yps magazine or Mickey Mouse magazine. Artemia franciscana, which is widely distributed and mainly used as a food animal, comes from North America, where it is found in the Great Salt Lake in Utah, among other places.
Food
Brine shrimp eat microalgae and animal microorganisms. In the Artemia breeding tank they can be fed, for example, with liquid algae solution (Liquizell or similar) or with algae powder (microcell, spirulina and so on) and occasionally with a slurry of dry yeast or with fresh yeast.

Survival
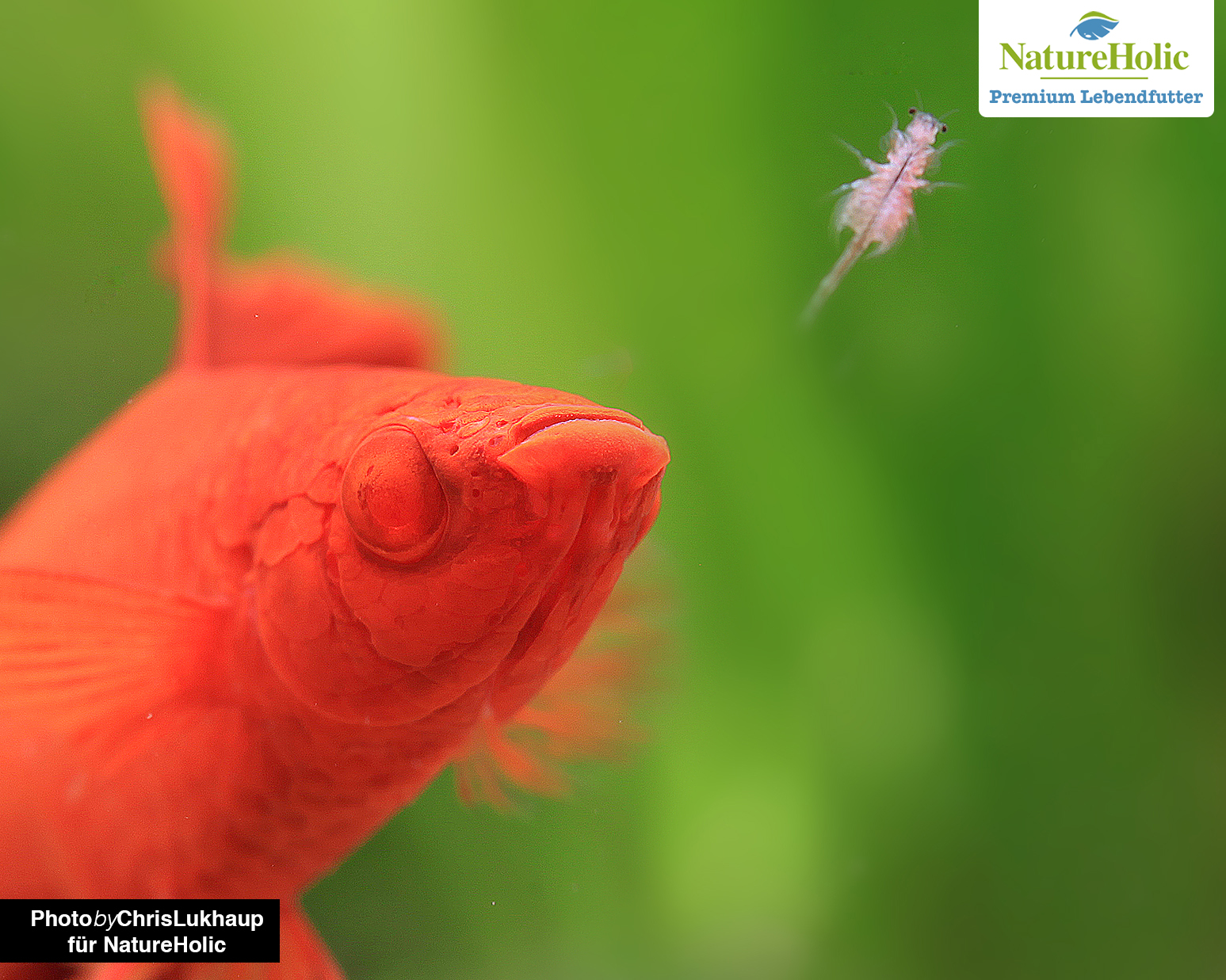
They have developed effective ways to allow their species to continue to exist despite drying habitats - they form permanent eggs that can lie dry for years, which is taken advantage of when breeding them as fish food. The tiny Artemia nauplii are excellent rearing food for fish larvae and also a good food for nano fish like guinea fowl and co. It is best to store Artemia eggs in the freezer, so the hatching rate remains high even after years.
Locomotion
Adult Artemia grow to 1-2 cm, whereas the nauplii remain much smaller. With their many leaf feet, the small crustaceans row through the water and thus offer fish a great hunting experience. The nauplii also twitch through the water and are gladly chased by fish larvae.
Who eats Artemia?
Adult Artemia are a suitable live food for small, medium to large fish and for all invertebrates in freshwater. The tiny Artemia nauplii are the rearing food par excellence for fish larvae and fry and also a good live food for nano fish.
Breeding kit
For an extensively running breeding stock, from which small amounts of Artemia and nauplii can be taken again and again, you need a transparent container of about 5 l capacity (or more - some simply put an old 250 liter aquarium in the garden). Substrate can be used, but does not have to be. Sunlight is conducive to algae growth. Salt water is needed here, for this purpose it is best to salt the breeding tank with sea salt from the pet store. Sea salt from the supermarket contains anti-caking agents, which are supposed to prevent sticking, but unfortunately make the gill leaves of the brine shrimp useless and thus suffocate the animals. The salt content of the water should be between 30 g/l and 70 g/l.

Value
Artemia contain an optimal mix of protein, carbohydrates and fats, and they are quite high in fiber - an excellent food for fish and invertebrates!
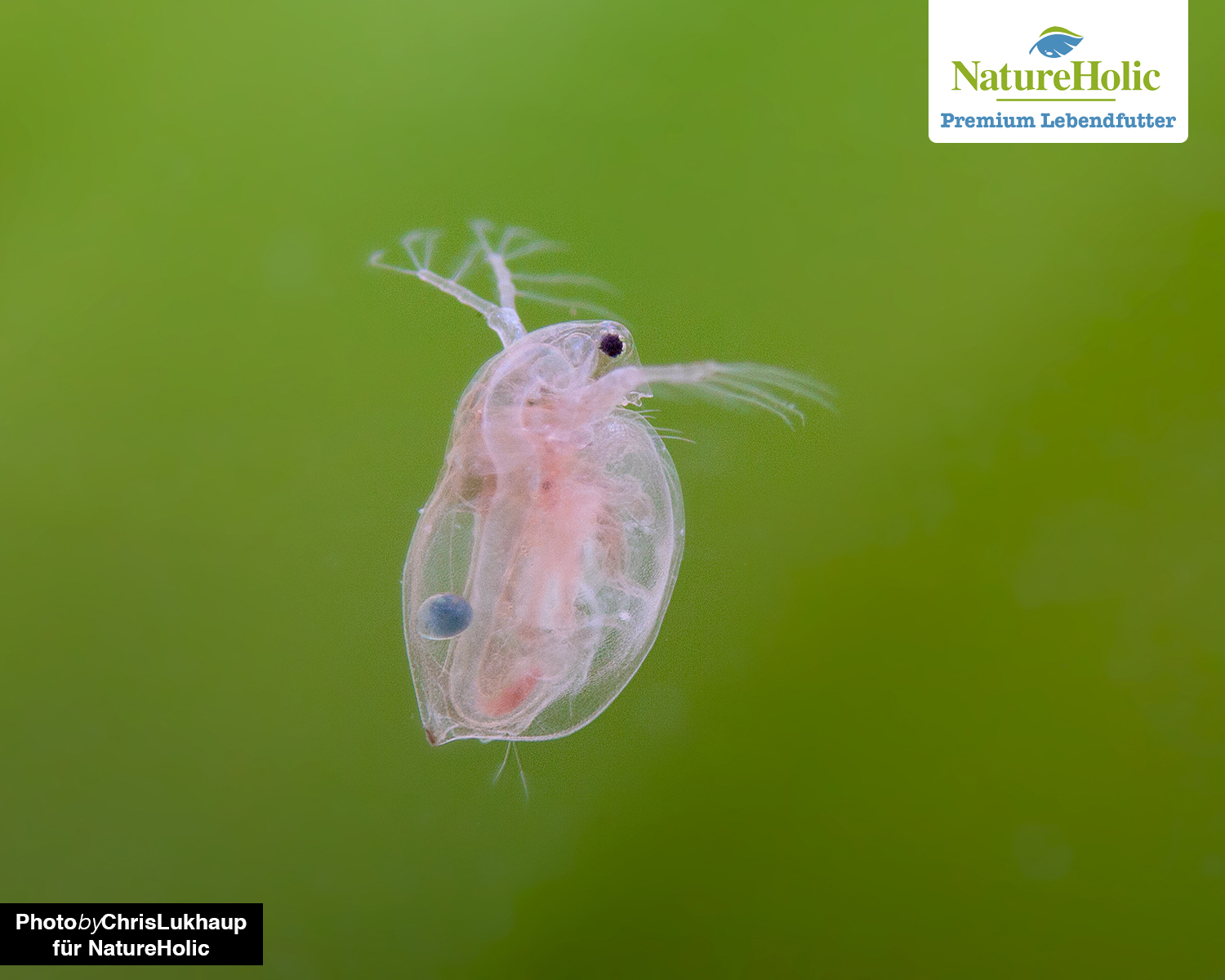
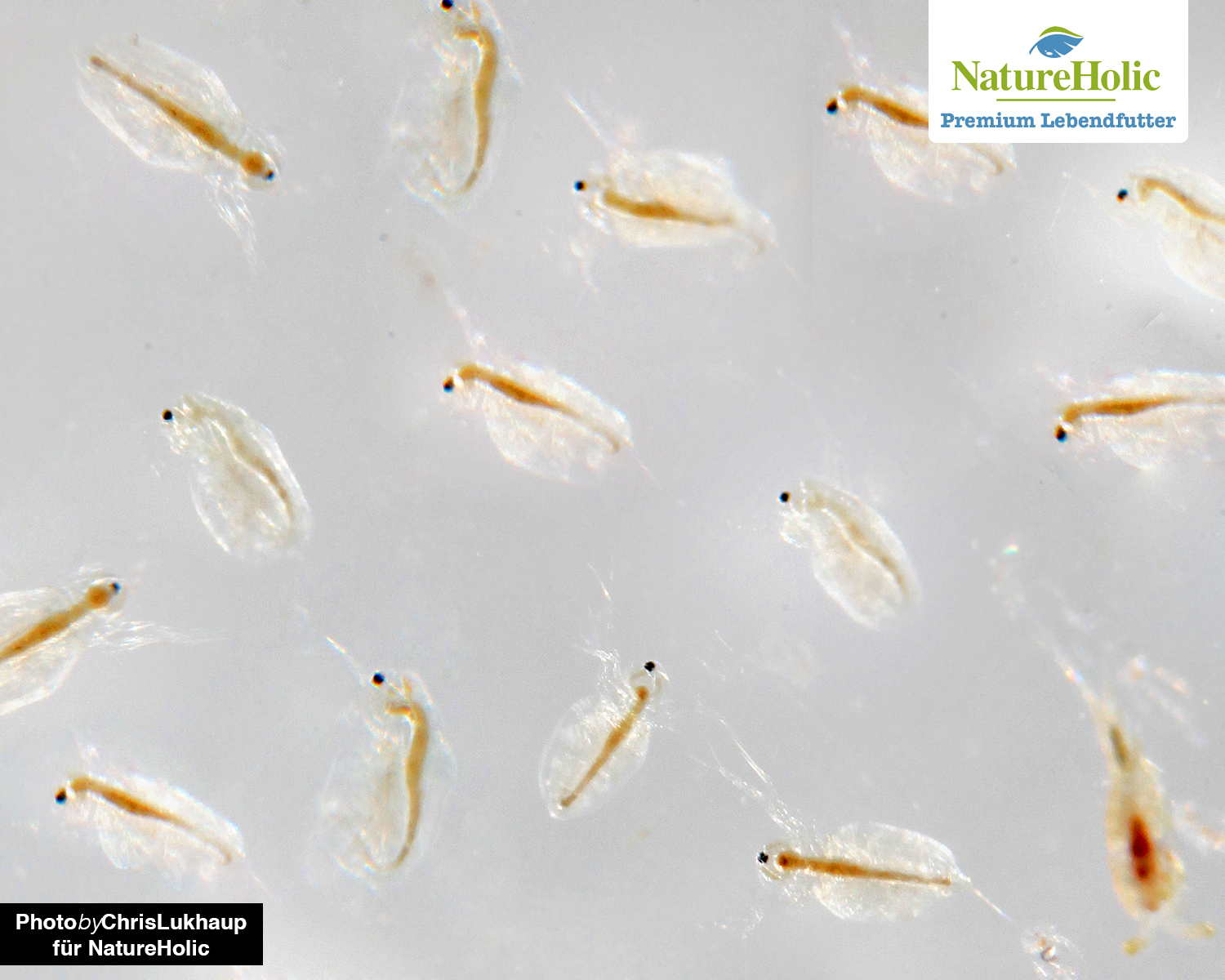
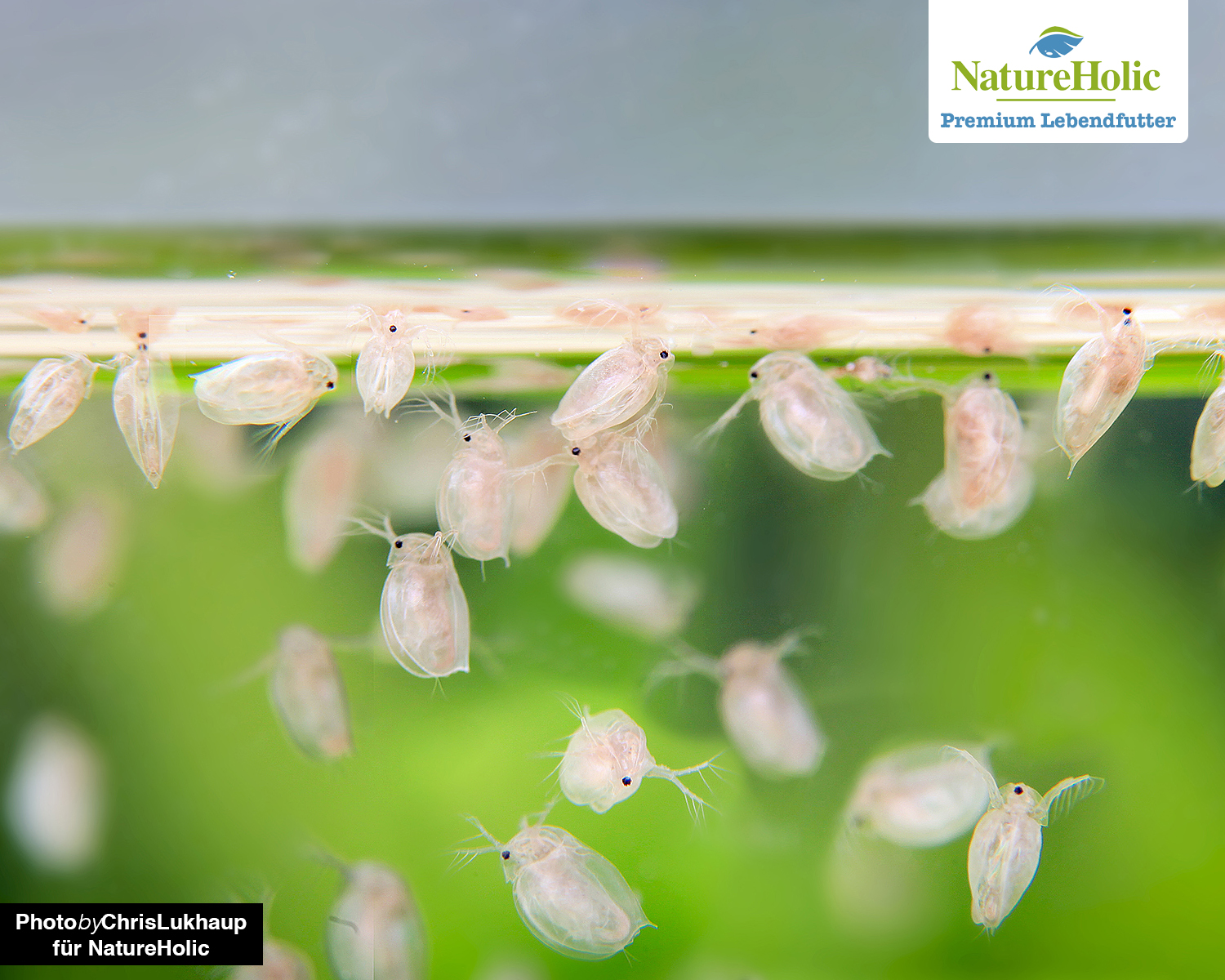
Water fleas / Daphnia(buy)
Water fleas are a very good live food for fish and crustaceans because they contain a lot of chitin, providing fiber for healthy digestion and starting materials for a stable exoskeleton in invertebrates. Daphnia contain very little fat and protein - so they are not suitable as a complete food, but they are very suitable as a low calorie, high fiber meal. Daphnia are rather spherical looking small crustaceans with a clearly visible eye and rudder arms. Daphnia do not last long in a filtered aquarium - they starve to death.
Locomotion
The water flea gets its name from its hopping mode of locomotion. It swims quite sluggishly, with current it has big problems.

Food
Water fleas feed as filter feeders on suspended algae and fine microorganisms.
Who eats water fleas?
All fish, but also shrimps, crayfish, dwarf crayfish and crabs. Even water fleas that are not immediately caught and eaten in an invertebrate aquarium are utilized once they have died - which does not take long in a flow-rich aquarium with clean water. In a tank without technical equipment, on the other hand, water fleas can be used very well as cleaners, which clean the water from floating algae and from bacteria and other small organisms by their filtering activity.
Breeding kit
Water fleas are extremely easy to breed - they are kept in a container with water. Substrate or plants are not necessary. It is important to add some bubble snails or post horn snails, which take care of skinning remains and possibly dead daphnia. Feed with slurried dry yeast, with spirulina powder, but also (very little) blood is a good food for water fleas. It is important to add only enough food to the water so that it becomes slightly cloudy and to feed only when the water is clear again. If too much food is added, there is a risk that the batch will tip over and the fleas will die.
The container can be placed outdoors or indoors. There is hardly any odor nuisance if you feed properly.

Value
In terms of nutritional content, water fleas are not particularly high, but they contain vitamins A and B2 and a lot of fiber.
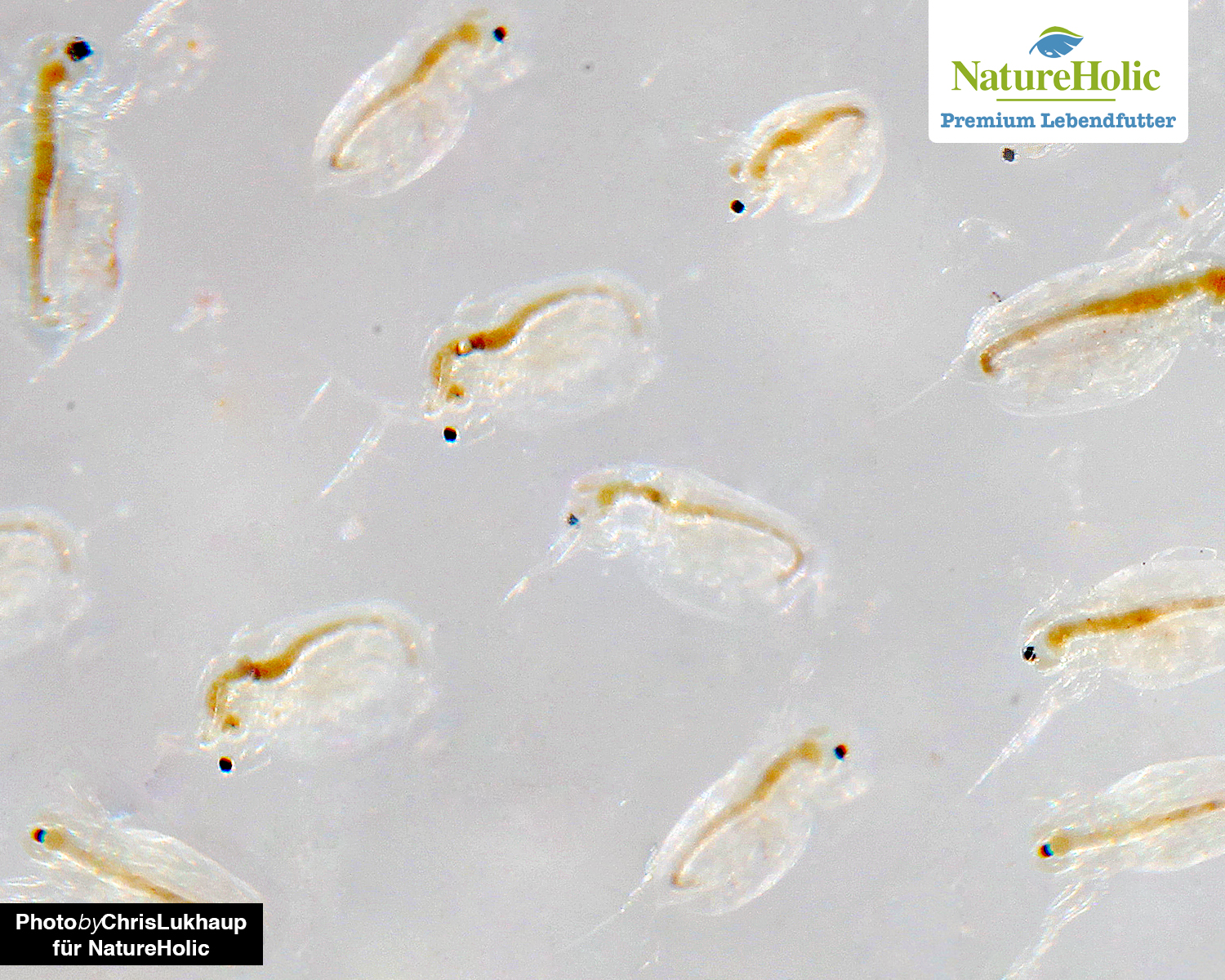
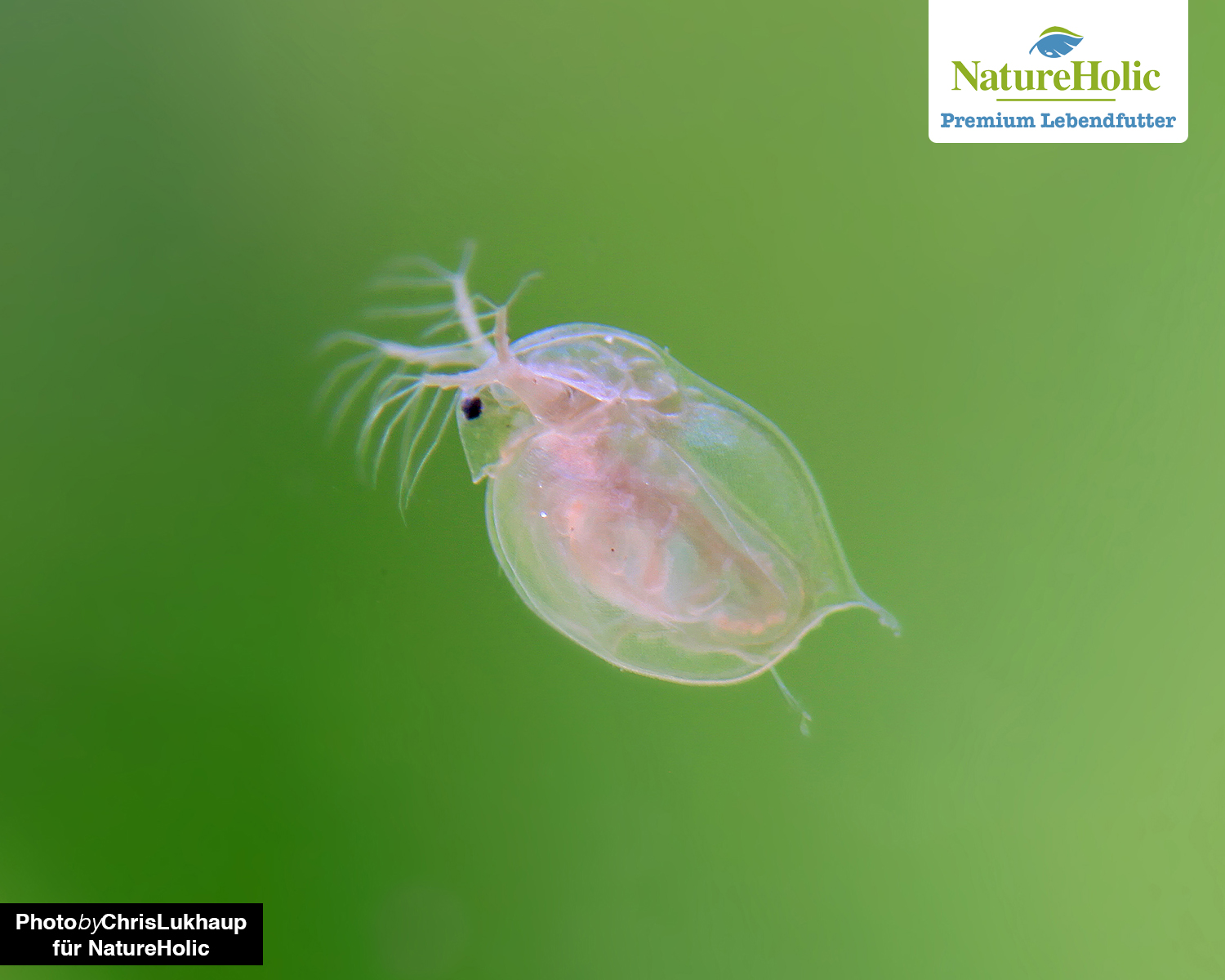
Moina salina - sea water flea(buy)
The sea water flea is a species native to southern Europe in salt flats, which needs salt water to survive. The advantage of feeding saltwater animals in a freshwater aquarium is that you are guaranteed not to introduce parasites and other unwanted co-inhabitants that can survive in freshwater, and also that uneaten live food animals will then die and cannot settle in the aquarium. At the latest then they are also eaten by shrimps and by snails or by small crustaceans.
Locomotion
Like Daphnia, Moina have two rowing feet with which they perform ponderous hopping movements in the water.
Food
Moina salina is a filter feeder and feeds on microorganisms and unicellular algae such as Nannochloropsis or Spirulina. Slurried dry yeast is also a very good food for marine fleas.

Who eats Moina salina?
Moina salina remain relatively small and are therefore a very good natural food for small to medium sized fish and for shrimps, smaller crabs and also dwarf crayfish and young crayfish.
Breeding kit
An aquarium from 20 liters is well suited for the further breeding of Moina salina. Important is a water temperature of 20-25 °C. Make sure that the salt content of the breeding tank does not deviate from the one in the bag - use a hydrometer to determine it if necessary. If the variation is too great, Moina salina will die. A salinity of 30-33 g per liter is usually good for permanent breeding of the marine flea. Under good conditions this water flea reproduces extremely well.

Value
Moina salina are high in fiber thanks to their chitinous shell, and they contain provitamin A. Their protein content and fat content are relatively low.
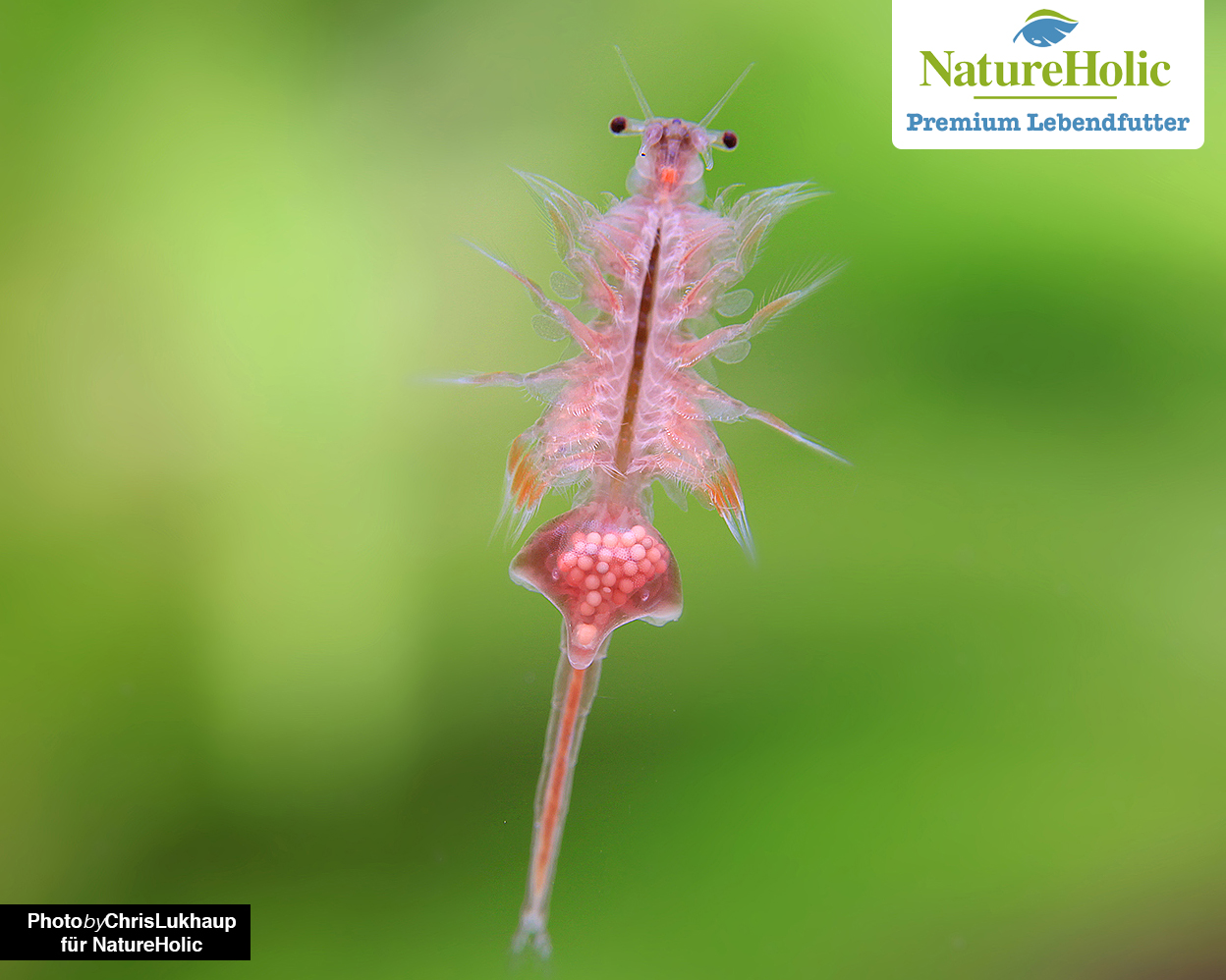
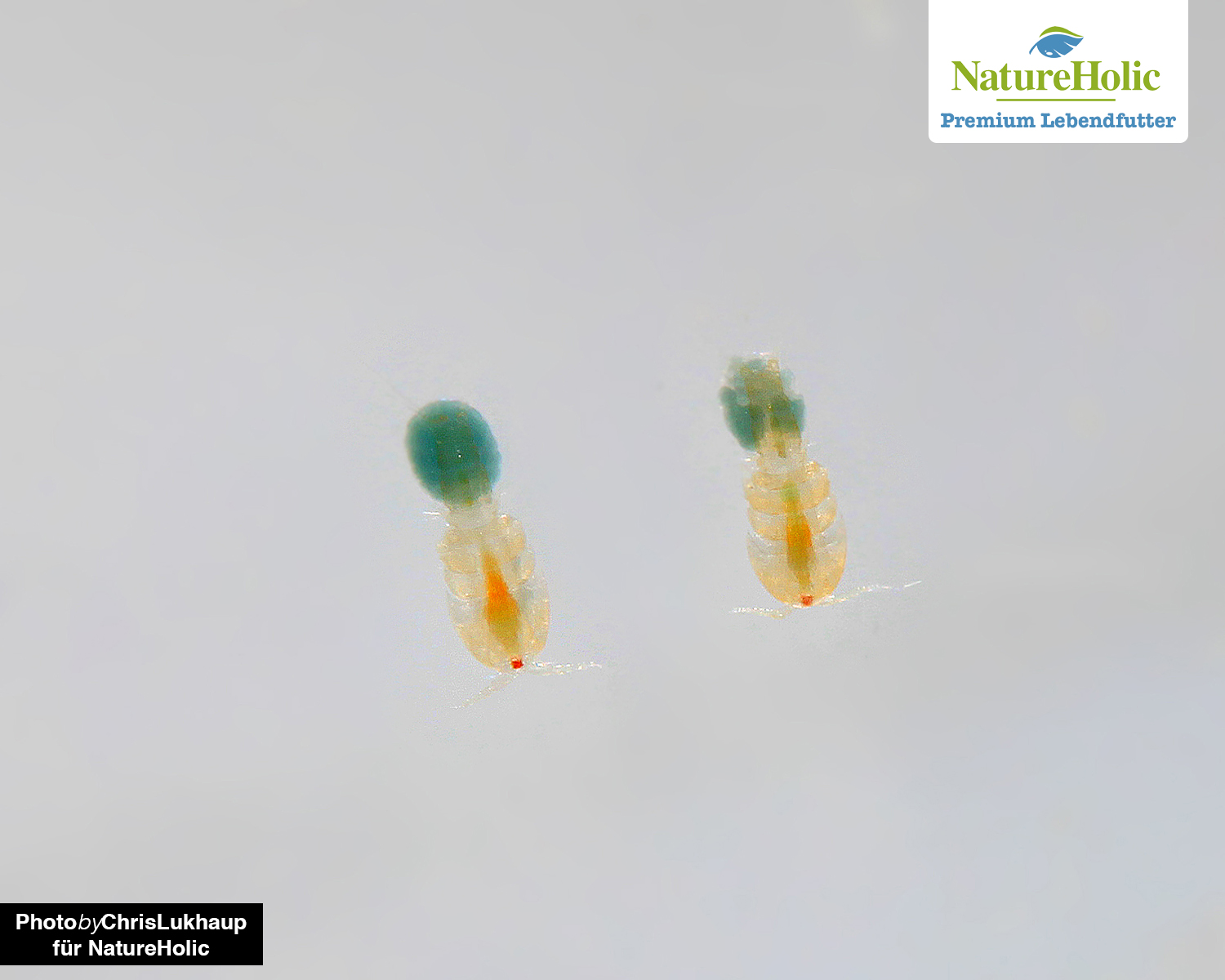
Marine copepods(buy)
Cyclops (jumping fish), which are well known from freshwater, also belong to the copepod family, so they are relatively closely related to marine copepods. However, marine copepods can be cultured much more effectively than Cyclops. This is good because these small crustaceans are the perfect fish food in terms of their composition of fats and protein, and also provide ideal ingredients for shrimp and other crustaceans - including chitin and omega-3 fatty acids, which are incredibly important for the development of young fish and crustaceans.
Thanks to their saltwater origins, freshwater aquariums don't catch parasites - stowaways simply die off.
Locomotion
Copepods belong to the copepod family. They have two little arms with which they "scoop" their way through the water, which causes the typical twitching swimming style.

Food
Copepods are small predators and eat unicellular marine algae such as Rhodomonas, Dunaliella and Isychrysis or a mixture of algae, as well as bacteria and other protozoa.
Who eats marine copepods?
Copepods, which remain small, and their nauplius larvae are very suitable as initial food for fish larvae. "Harvest" copepods with sieves of various mesh sizes, depending on their size. We recommend 20 µm, 50 µm, 100 µm and 250 µm, possibly 1000 µm. Especially for the breeding of marine animals like seahorses and others, live copepods are indispensable for feeding! But also fish larvae in fresh water benefit from these tiny crustaceans. By the way, they do not contain more salt inside their bodies than freshwater hoppers! Before feeding them in freshwater aquariums, please rinse well to remove salt residues.
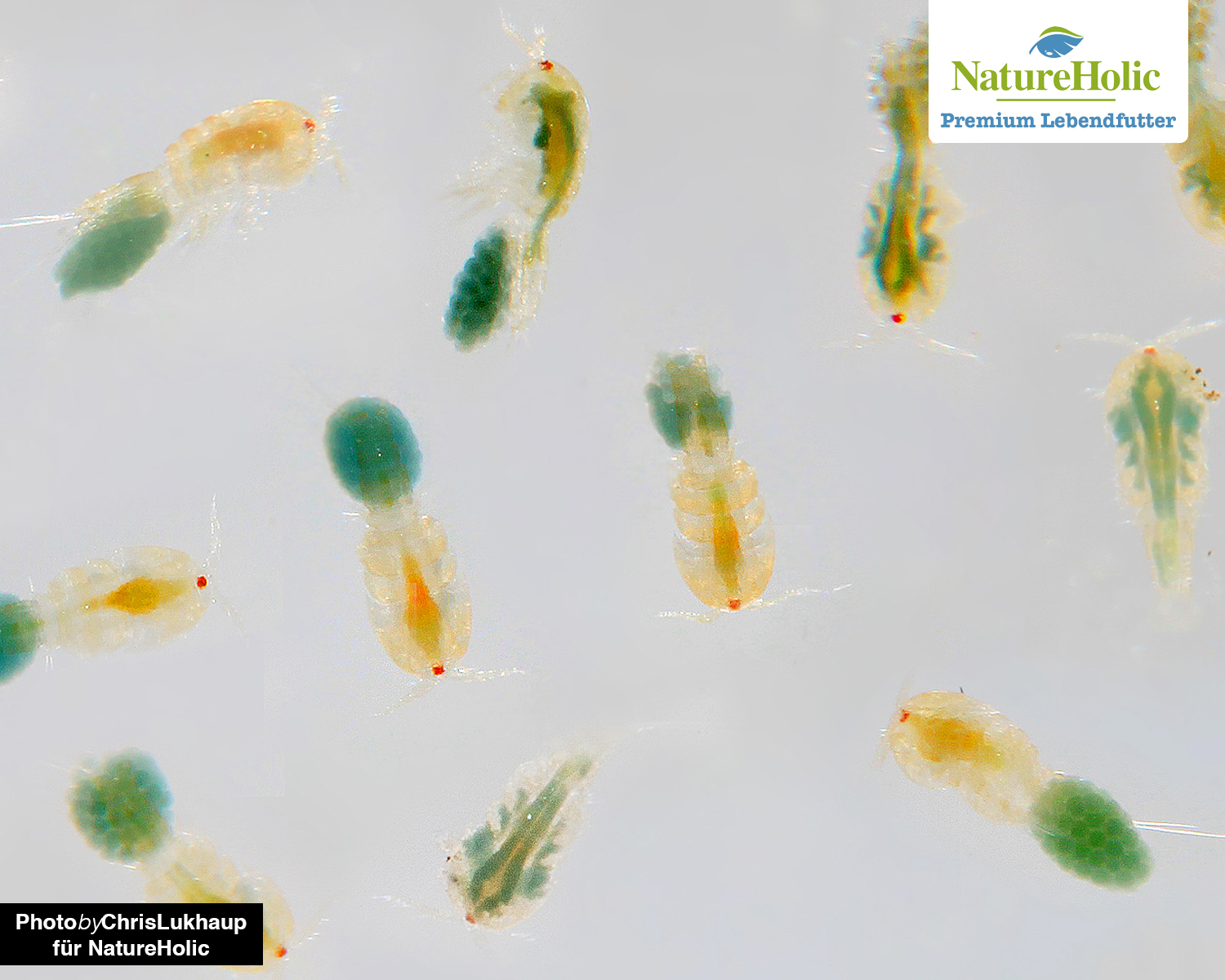

Breeding kit
Marine copepods are somewhat more difficult to breed than other live foods due to their feeding habits. You should at least have a good algae culture going to be able to feed them properly. Once this is given, all you need is an aquarium with a capacity of about 20 liters and sea salt from a specialty store. An air lifter provides the necessary water circulation.
Value
In terms of composition and size, marine Copeopden are ideal fish food. Many marine animals cannot be bred at all or only with great difficulty without copeopden.
Oceanic cephalopod(buy)
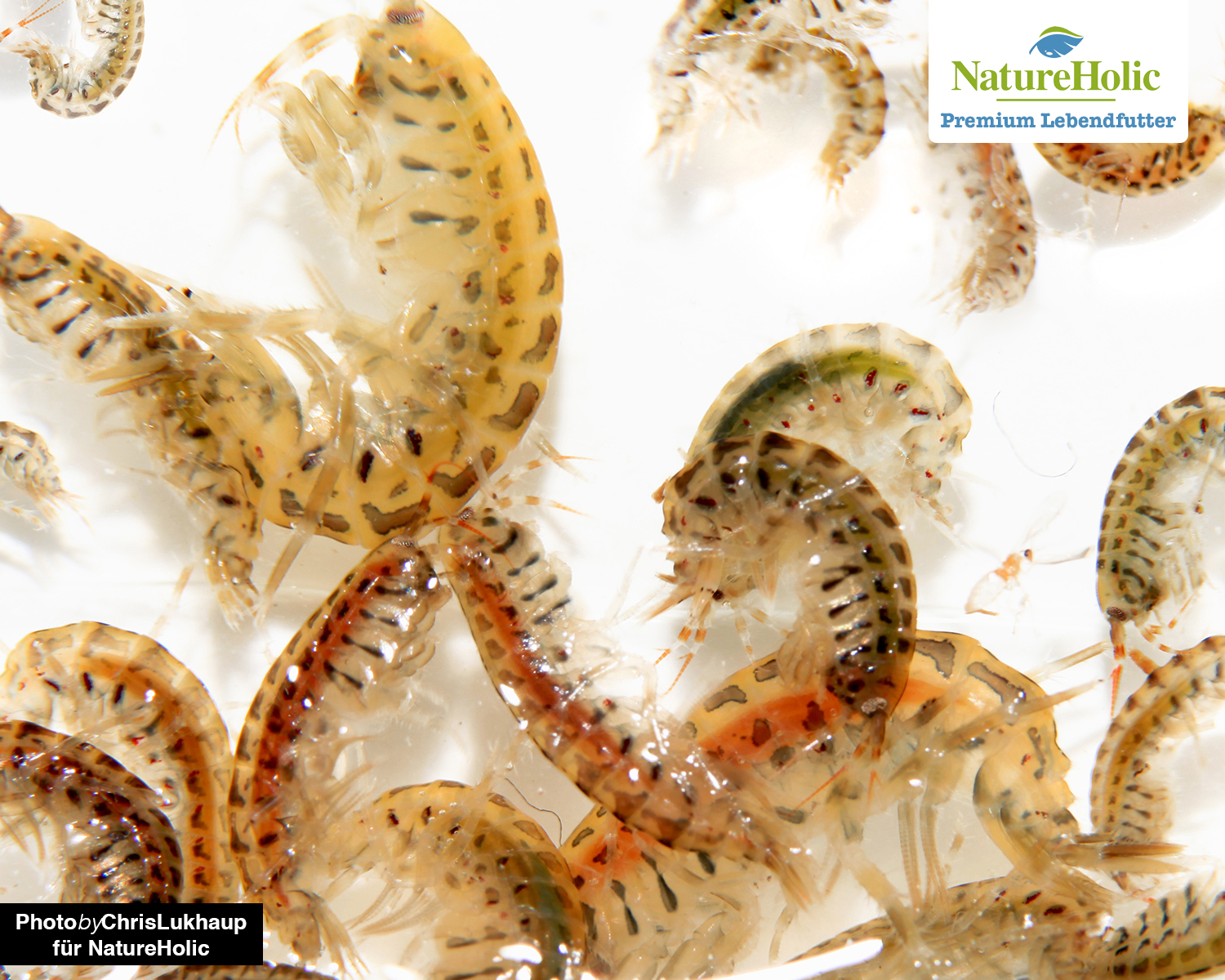
Gammarus oceanicus, the oceanic crayfish, lives among others from the Baltic Sea, where it occurs in brackish water areas with a salinity of 2 to 20 g salt per liter. However, it is generally widespread along the coasts of the Atlantic Ocean - from northern Europe to North America these gammarids can be found. The oceanic amphipods grow up to 3 cm in length, so they are quite a bit larger. The oceanic amphipod reproduces in the Baltic Sea once a year. The young animals become sexually mature in October, the eggs hatch from May. Breeding in the aquarium is possible, here it can even come to 2-3 reproductive cycles per year. In fresh water the amphipods die sooner or later, which makes them usable by shrimps and snails.
Locomotion
Like all amphipods this Gammarus swims and crawls actively.
Food
Gammarus oceanicus is omnivorous and eats detritus, live and dead plants, as well as algae, microorganisms, worms, crustaceans and carrion.

Who eats oceanic psyllids?
As a live food, Gammarus ocenanicus can be used more for larger fish and also for large crayfish and crabs. Of course, the offspring is also suitable for feeding to smaller fish, crabs and crayfish.
Breeding kit
In a brackish water aquarium from 54 liters with a salt content of about 10-20 g sea salt per liter Oceanic Flea Crayfish can be bred well, even if you certainly should not expect mass reproduction here. Attention, the animals can bite painfully if they feel threatened! The substrate should be covered with large pebbles, because the amphipods prefer hard substrate.
Value
Due to their excellent composition of protein, fat and fiber, Gammarus oceanicus are an excellent live food primarily for large fish, large crayfish and large crabs. Juveniles of oceanic crayfish can also be fed to smaller fish. In freshwater these Gammarus eventually die, and at the latest then they are also eaten by shrimps and snails.
Feeder shrimp / Palaemon varians(buy)
The feeder shrimp or rock shrimp Palaemon varians originates from the Baltic Sea and the North Atlantic and the Mediterranean Sea. It can be kept in light brackish water to seawater, even in freshwater it survives for quite a while, but eventually dies. When fully grown they grow to a length of about 6 cm.
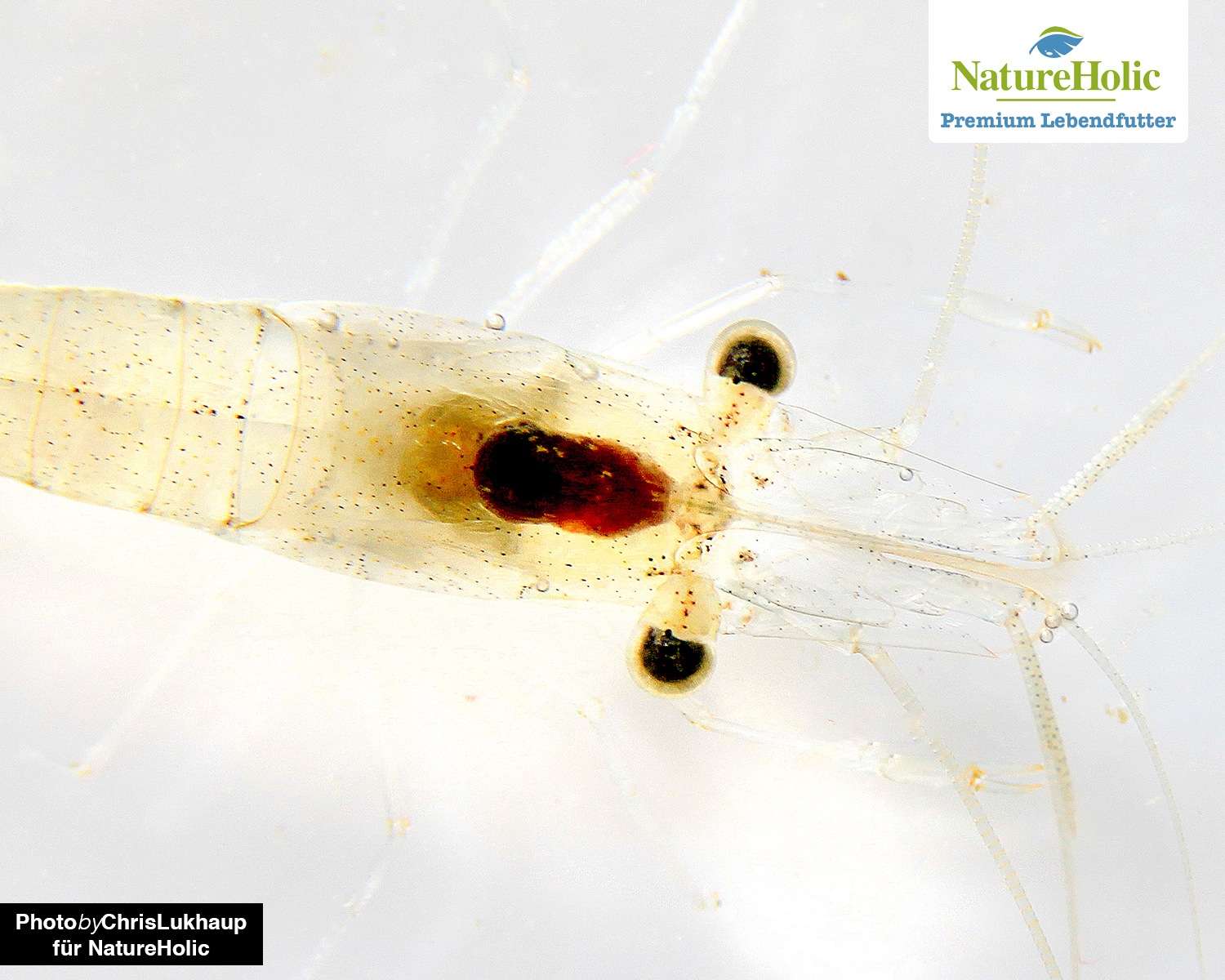

Locomotion
Feeding shrimps move crawling and swimming.
Food
Palaemon varians is an omnivore, but prefers a larger portion of meaty food. Shrimp food is well suited, but also frozen food, protein food and so on.
Who eats food shrimp?
All larger carnivorous fish will readily accept feeder shrimp. Crayfish and dwarf shrimp do not go for them. Since they can survive for quite some time in freshwater aquariums, they will not take advantage of an early demise.
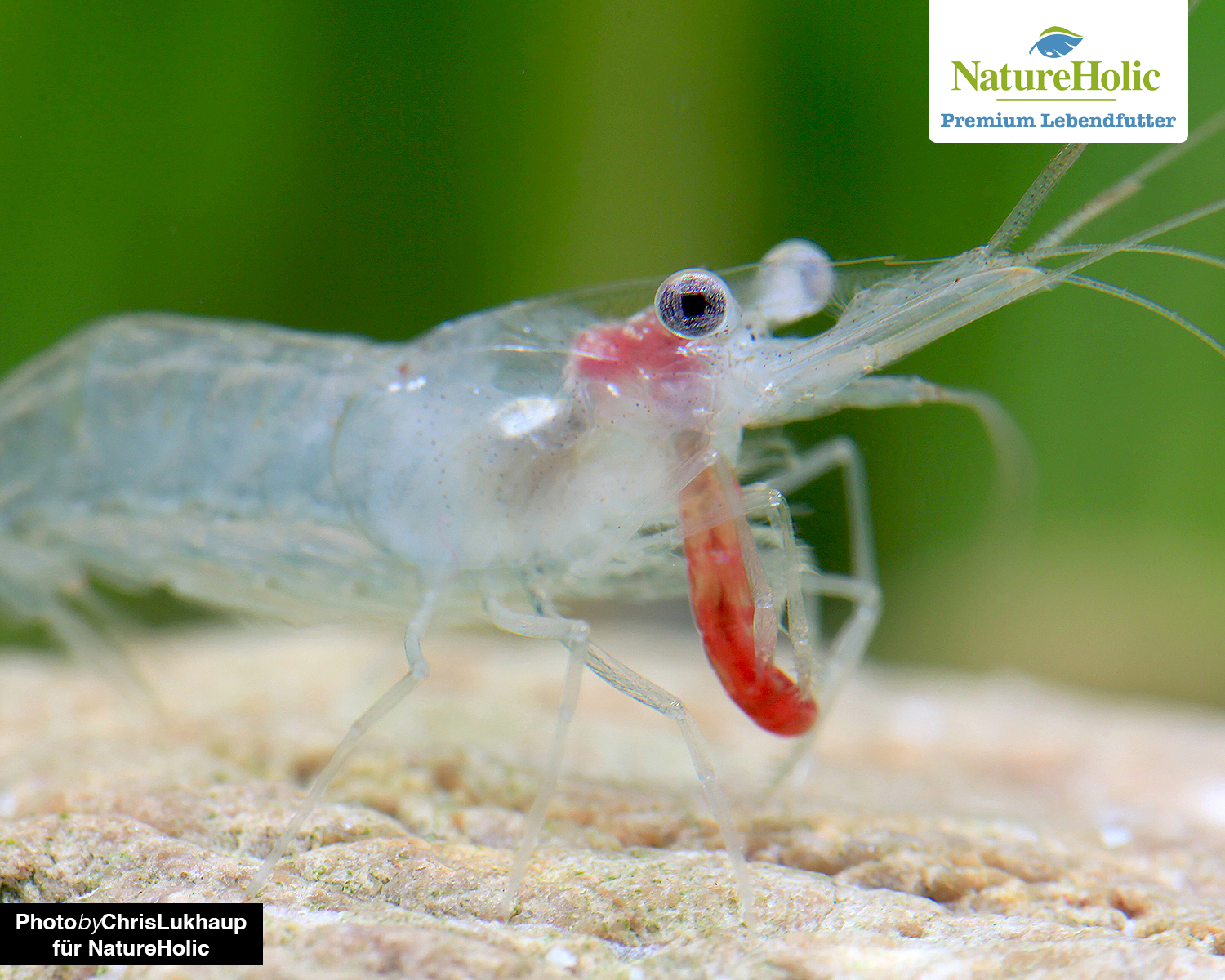

Breeding kit
Feeding shrimps are very difficult to reproduce in the aquarium in such numbers that they could be used as a permanent food source. They belong to the primitive reproduction type and release larvae.
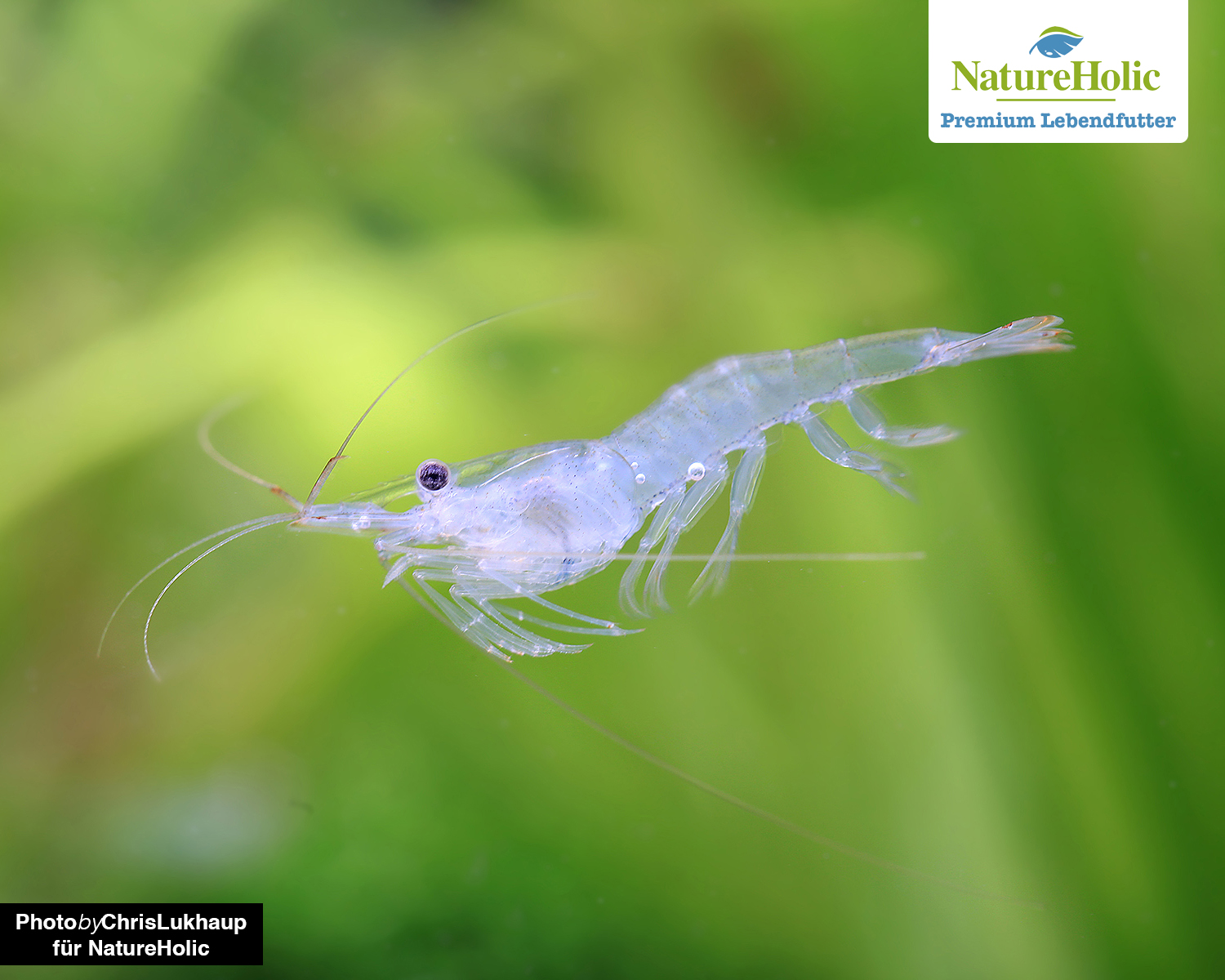

Value
The ratio of nutrients and fiber is excellent in forage shrimp, they are a very good food for larger fish.







